High GI vs Moderate GI
vs Low GI Foods
A Comprehensive Comparison
Glycemic Index (GI) is a fundamental tool for understanding how various foods affect blood sugar levels. It categorizes foods into three major groups: High GI, Moderate GI, and Low GI. Let's explore the key differences between these categories, along with their typical GI values, in the table below:
| Aspect | High GI Foods | Moderate GI Foods | Low GI Foods |
|---|---|---|---|
| GI Range | 70 and above | 56 to 69 | 0 to 55 |
| Blood Sugar Impact | Rapid and substantial rise | Gradual increase | Slow and steady rise |
| Energy Release | Quick energy spike | Moderate, sustained energy | Sustained, lasting energy |
| Satiety | Short-lived fullness | Satisfying, but shorter fullness | Longer-lasting fullness |
| Recommended for | Athletes, quick energy needs | General population, athletes | Diabetics, Weight Watchers |
| Example of Foods | White bread, Sugary cereals, Soda | Whole wheat bread, Brown rice. White rice(Short-grain) | Oats, Quinoa, Lentils, Sweet Potatoes, Most Vegetables |
Key Takeaways
High GI Foods: These foods have a GI value of 70 or above, resulting in a rapid and substantial rise in blood sugar levels. They are typically recommended for athletes or individuals with immediate energy needs. High GI foods provide a quick energy spike but are not ideal for sustained energy or long-lasting fullness.
Moderate GI Foods: Falling within the GI range of 56 to 69, moderate GI foods lead to a gradual increase in blood sugar levels. They are suitable for the general population and athletes who require moderate, sustained energy. While these foods are satisfying, the feeling of fullness may not last as long as with low GI options.
Low GI Foods: These have a GI value of 0 to 55, resulting in a slow and steady rise in blood sugar levels. They are highly recommended for diabetics and individuals looking to manage their weight. Low GI foods provide sustained and lasting energy, making them ideal for those who want to maintain stable blood sugar levels throughout the day.
Individual responses to GI values can vary based on factors such as portion size, food combinations, and overall diet.
Graph and Chart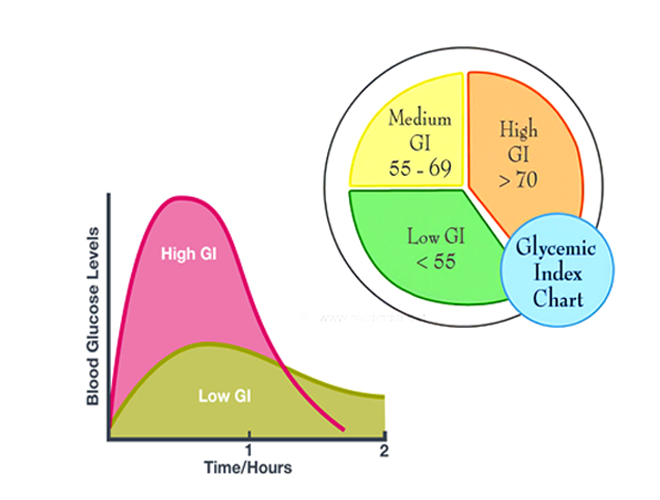

Conclusion
Understanding the distinctions between high GI, moderate GI, and low GI foods is essential for making informed dietary choices. Tailoring your diet to your specific health and fitness goals becomes more accessible when you consider the impact of GI values on your blood sugar levels.
Disclaimer: This article contains affiliate links to products that can assist you in incorporating high GI, moderate GI, and low GI foods into your diet. We may earn a commission if you make a purchase through these links, at no extra cost to you. Your support helps us continue to provide valuable information on nutrition and healthy eating.






0 Comments